06. Angle of Arrival Introduction
Angle of Arrival Introduction
Phased Array Antenna
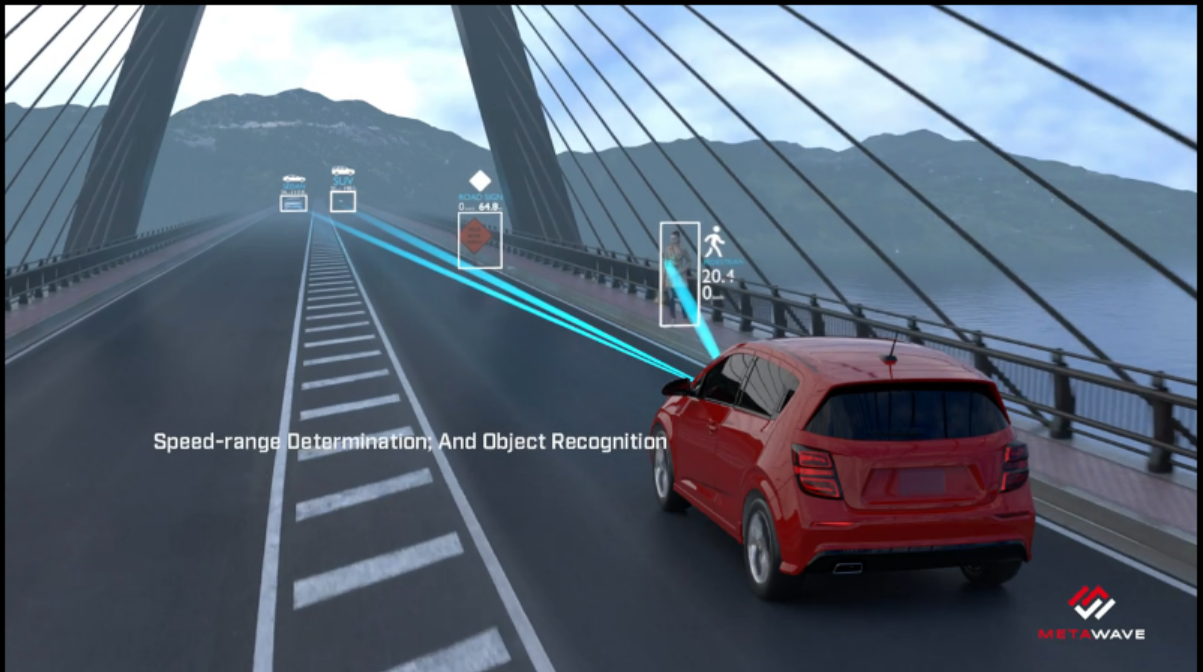
Metawave’s Beam Steering Radar
Phase Array Introduction Heading
A phased array antenna is an antenna array that steers the beam electronically in the desired direction. The array steers the beam if each antenna element in an array is excited by the signal with certain phase values. This phenomenon is referred to as beam scanning.
Beam Scanning Radar
Beam Steering Design. Here the \Phi represents the phase shifters. Phase shifters are the electronic components that changes the phase to make the beam steer in a desired direction.
source : analog.com
Beam Steering Radar
For antenna beam to steer in a desired direction, the phase shifters are programmed to have constant phase increments. If an antenna comprises of six radiating elements and the phase delta required to steer a beam in a given direction is 15 degrees, then the following would be the phase value on each element [0,15,30,45,60,75] degrees. The increment phase shift along with the spacing between antenna elements (d) determines the steering angle of an antenna using the following equation
- \Phi= incremental phase shift
- d = spacing between antenna elements
- \theta= steering direction from the normal of the antenna surface
- \lambda= wavelength of the signal
As the radar scan the surroundings by steering the beam at the programmed angles, it can sense the angle of the return signal. This helps Radar create a spatial perception of the environment.
Phase Array Graphic

Radar Module for Automotive Applications from D3 Engineering
Angle of Arrival
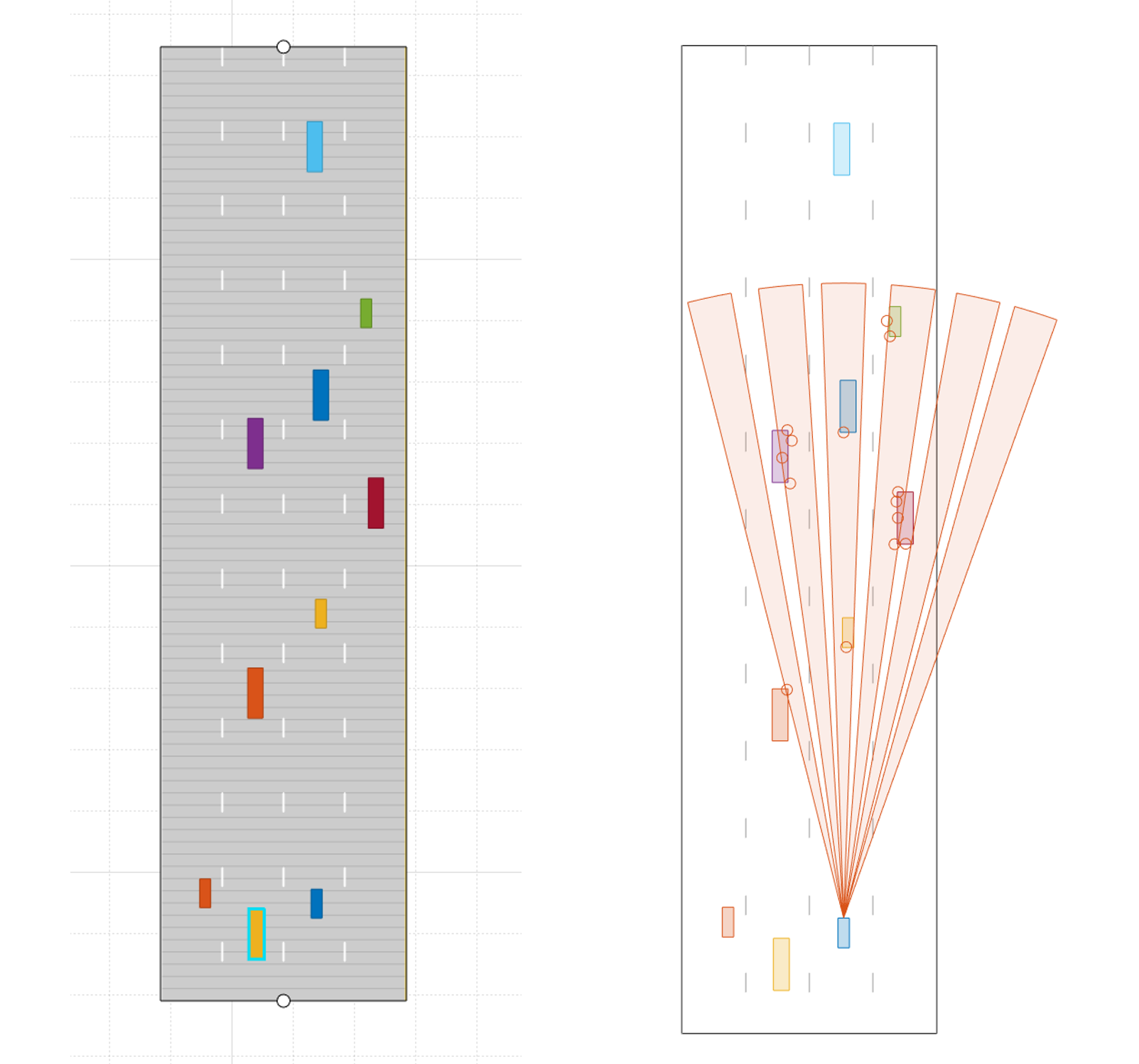
Road scenario for beam steering radar
As the radar scans the surroundings by steering the beam at the programmed angles, it measures the SNR of reflected signals from targets located at different angles spatially. This helps in creating an angle of arrival vs SNR grid for radar’s spatial perception.

Further Research
For more information about phased array antennas see here .